
Atomic Number of Argon is 18.
Chemical symbol for Argon is Ar. Number of protons in Argon is 18. Atomic weight of Argon is 39.948 u or g/mol. Melting point of Argon is -189,4 °C and its the boiling point is -185,9 °C.
» Boiling Point» Melting Point» Abundant» State at STP» Discovery Year
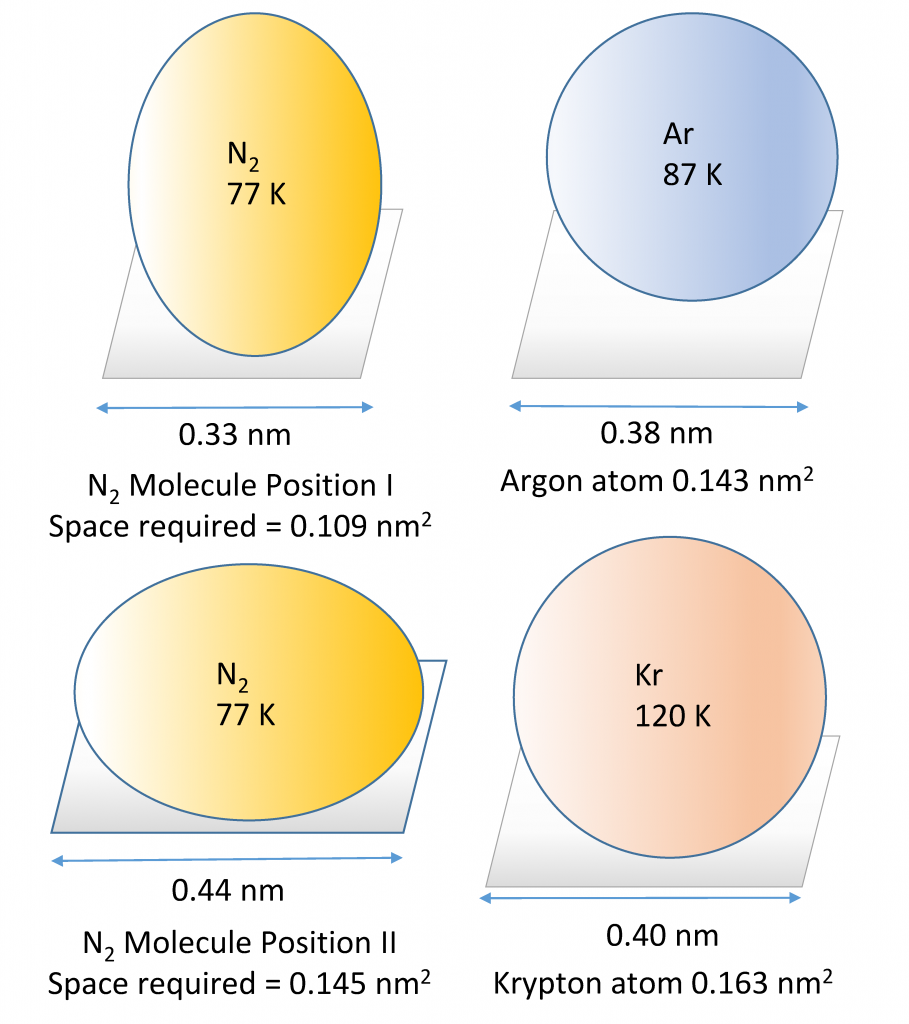
Argon is a chemical element with atomic number 18 which means there are 18 protons and 18 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Argon is Ar. Atomic Mass of Argon Atomic mass of Argon is 39.948 u. Image showing periodicity of valence s-orbital radius for the chemical elements as size-coded balls on a periodic table grid. The R max values for neutral gaseous element valence orbitals are abstracted from reference 1. Mann, Atomic Structure Calculations II.Hartree-Fock wave functions and radial expectation values: hydrogen to lawrencium, LA-3691, Los Alamos Scientific.
Argon Atom Model

About Argon
Argon is a gas without color and odor, which is one of the noble gases and is totally not reactive with other elements of the Periodic Table. The name of this chemical element originates from the Greek word meaning idle. There is some argon in its pure form in the atmosphere of our planet (estimated to be a little less than 1 per cent) but it has no high biological importance. Argon turns light violet when electricity passes through it. It is used in welding as well as in light and fluorescent bulbs. Also, argon is used to fill up space between two panes of the double glazed windows.
Group 18 elements (helium, neon, and argon are shown) have a full outer. Bohr Model Of Argon Atom Potassium Atom, Copper Atom, Atom Model Project, Bohr. Visit chemical elements, crystals, melting points, Bohr Model of Copper. Bohr diagrams indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell.
Uses of Argon
Argon is the third element of the eighteenth column of the period table. It is classified as a noble gas. The argon atom has 18 electrons and 18 protons. Its outer shell is full with eight electrons. Characteristics and Properties Under standard conditions argon is an odorless and colorless gas. Argonium (ArH +) is an ion combining a proton and an argon atom. It is found in interstellar space in diffuse atomic hydrogen gas where the fraction of molecular hydrogen H 2 is in the range of 0.0001 to 0.001. Argonium is formed when H 2+ reacts with Ar atoms.
Argon, inert gas with the symbol Ar, is used in radio tubes, Geiger counters, fluorescent tubes, and incandescent light bulbs. It is also used in double-glazed windows to fill the space between the panes. And it is used in the production of some metals like titanium, uranium, and zirconium.
Argon can be used in neon lights, heat-treating processes, scientific research, medicine, and 3-D printing too.
Compounds with Argon
- HArF: Argon fluorohydride
- ArH+: Argonium
- MgAr+: Magnesium argide
Properties of Argon Element
| Atomic Number (Z) | 18 |
|---|
| Atomic Symbol | Ar |
|---|
| Group | 18 |
|---|
| Period | 3 |
|---|
| Atomic Weight | 39.948 u |
|---|
| Density | 0.0017837 g/cm3 |
|---|
| Melting Point (K) | 83.8 K |
|---|
| Melting Point (℃) | -189,4 °C |
|---|
| Boiling Point (K) | 87.3 K |
|---|
| Boiling Point (℃) | -185,9 °C |
|---|
| Heat Capacity | 0.52 J/g · K |
|---|
| Abundance | 3.5 mg/kg |
|---|
| State at STP | Gas |
|---|
| Occurrence | Primordial |
|---|
| Description | Noble gas |
|---|
| Electronegativity (Pauling) χ | no data |
|---|
| Ionization Energy (eV) | 15.75962 |
|---|
| Atomic Radius | 71pm |
|---|
| Covalent Radius | 97pm |
|---|
| Van der Waals Radius | 188 |
|---|
| Valence Electrons | 8 |
|---|
| Year of Discovery | 1894 |
|---|
| Discoverer | Ramsay and Rayleigh |
|---|
What is the Boiling Point of Argon?
Argon boiling point is -185,9 °C. Boiling point of Argon in Kelvin is 87.3 K.
What is the Melting Point of Argon?
Argon melting point is -189,4 °C. Melting point of Argon in Kelvin is 83.8 K.
How Abundant is Argon?
Abundant value of Argon is 3.5 mg/kg.
What is the State of Argon at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)?
State of Argon is Gas at standard temperature and pressure at 0℃ and one atmosphere pressure.

When was Argon Discovered?
Argon was discovered in 1894.
Chemical properties of argon - Health effects of argon - Environmental effects of argon
Argon Atomic Mass
18 | Atomic mass | 39.948 g.mol -1 | Electronegativity according to Pauling | unknown | Density | 1.78.10 -3 g.cm -3 at 0 °C | Melting point | -189 °C | Boiling point | -185.7 °C | Vanderwaals radius | 0.192 nm | Ionic radius | unknown | Isotopes | 6 | Electronis shell | [Ne] 3s23p6 | Energy of first ionisation | 1520 kJ.mol -1 | | Energy of second ionisation | 2665.8 kJ.mol -1 | | Energy of third ionisation | 3931 kJ.mol -1 | Discovered by | Sir Ramsay in 1894 |
|
Argon
Argon was suspected to be present in air by Henry Cavendish in 1785 but wasn't discovered until 1894 by Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay. Argon is the third noble gas, in period 8, and it makes up about 1% of the Earth's atmosphere. Mozilla for mac 5. Argon has approximately the same solubility as oxygen and it is 2.5 times as soluble in water as nitrogen . This chemically inert element is colorless and odorless in both its liquid and gaseous forms. It is not found in any compounds. This gas is isolated through liquid air fractionation since the atmosphere contains only 0.94% argon. The Martian atmosphere in contrast contains 1.6% of Ar-40 and 5 ppm Ar-36. World production exceeds 750.000 tonnes per year, the supply is virtually inexhaustible. Applications Argon does not react with the filament in a lightbulb even under high temperatures, so is used in lighting and in other cases where diatomic nitrogen is an unsuitable (semi-)inert gas.
Argon is perticularly important for the metal industry, being used as an inert gas shield in arc welding and cutting. Other uses incude non-reactive blanket in the manufacture of titanium and other reactive elements and as a protective atmosphere for growing silicon and germanium crystals. Argon-39 has been used for a number of applications, primarily ice coring. It has also been used for ground water dating. Argon is also used in technical SCUBA diving to inflate the drysuit, due to its nonreactive, heat isolating effect.
Argon as the gap between the panes of glass provides better insulation because it is a poorer conductor of heat than ordinary air. The most exotic use of argon is in the tyre of luxury cars. Argon in the environment In earth's atmosphere, Ar-39 is made by cosmic ray activity, primarily with Ar-40. In the subsurface environment, it is also produced through neutron-capture by K-39 or alpha emission by calcium. Argon-37 is produced from the decay of calcium-40, the result of subsurface nuclear explosions. It has a half-life of 35 days. Argon is present in some potassium minerals because of radiactive decay of the isotope potassium-40 Health effects of argonRoutes of exposure: The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation. Inhalation risk:On loss of containment this liquid evaporates very quickly causing supersaturation of the air with serious risk of suffocation when in confined areas. Effects of exposure: Inhalation: Dizziness. Dullness. Headache. Suffocation. Skin: On contact with liquid: frostbite. Eyes: On contact with liquid: frostbite. Inhalation: This gas is inert and is classified as a simple asphyxiant. Inhalation in excessive concentrations can result in dizziness, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, and death. Death may result from errors in judgment, confusion, or loss of consciousness which prevent self-rescue. At low oxygen concentrations, unconsciousness and death may occur in seconds without warning. The effect of simple asphyxiant gases is proportional to the extent to which they diminish the amount (partial pressure) of oxygen in the air that is breathed. The oxygen may be diminished to 75% of it's normal percentage in air before appreciable symptoms develop. This in turn requires the presence of a simple asphyxiant in a concentration of 33% in the mixture of air and gas. When the simple asphyxiant reaches a concentration of 50%, marked symptoms can be produced. A concentration of 75% is fatal in a matter of minutes. Symptoms: The first symptoms produced by a simple asphyxiant are rapid respirations and air hunger. Mental alertness is diminished and muscular coordination is impaired. Later judgment becomes faulty and all sensations are depressed. Emotional instability often results and fatigue occurs rapidly. As the asphyxia progresses, there may be nausea and vomiting, prostration and loss of consciousness, and finally convulsions, deep coma and death. Environmental effects of argonNo known ecological damage caused by argon. Pomello. No adverse environmental consequences are expected. Argon gas occurs naturally in the environment. The gas will dissipate rapidly in well ventilated areas. The effects of argon on plants or animals is not currently known. It is not expected to harm aquatic life. How to add attachment to gmail on iphone. Use Move to iOS App. Apple developed a smooth solution for users converting from Android to iOS. IPhone & iPad Android Computer Open your iPhone or iPad's Settings app. Tap Accounts & Passwords Add Account Google. Enter your email and password. Argon does not contain any ozone depleting chemicals and is not listed as a marine pollutant by DOT (Department of Transportation, USA).
Now check out our page on argon in water Back to chart periodic elements |
More from 'Elements'
Lenntech (European Head Office)
Distributieweg 3
2645 EG Delfgauw
The Netherlands
Phone: +31 152 610 900
fax: +31 152 616 289
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech USA LLC (Americas)
5975 Sunset Drive
South Miami, FL 33143
USA
Phone: +1 877 453 8095
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech DMCC (Middle East)
Level 5 - OFFICE #8-One JLT Tower
Jumeirah Lake Towers
Dubai - U.A.E.
Phone: +971 4 429 5853
e-mail: info@lenntech.com

Copyright © 1998-2021 Lenntech B.V. All rights reserved





